In recent years, 3D printing has made significant strides in various industries, including healthcare, where its ability to create customized, patient-specific solutions has revolutionized medical practices. Personalized and precision medicine are two key fields where 3D printing has brought about groundbreaking changes, particularly in cancer treatment, orthopedics, dentistry, and ophthalmology. This article explores the deep applications of 3D printing in healthcare, focusing on how it is utilized to improve treatment outcomes and streamline surgical planning through the precise printing of human models.
1. Personalized and Precision Medicine: A New Frontier
Personalized medicine refers to the practice of tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, such as their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. Precision medicine builds upon this by using advanced technologies to understand and treat diseases at a molecular level. 3D printing plays a crucial role in both these areas by enabling doctors to design and manufacture customized medical devices and models specific to a patient’s anatomy and disease condition.
One of the core advantages of 3D printing in personalized medicine is its ability to create anatomically accurate, patient-specific models for surgical planning and intervention. With 3D printing services, healthcare providers can manufacture prosthetics, implants, and other medical devices with an exact fit to the patient’s body, ensuring a higher success rate in surgeries and treatments.
2. 3D Printing in Cancer Treatment: Revolutionizing Tumor Management
In the realm of cancer treatment, 3D printing has been a game changer, especially when it comes to surgical planning and personalized treatments. Tumors can vary greatly in size, shape, and location, and traditional imaging techniques may not provide the level of detail required for precise surgical interventions. However, 3D printing allows for the creation of accurate, three-dimensional models of tumors, providing surgeons with a tangible representation of the cancerous growth.
Using advanced 3D printing services, healthcare professionals can obtain 3D printed tumor models from MRI and CT scans. These models enable doctors to plan complex surgeries more effectively, allowing them to better understand the extent of the tumor and how to remove it while preserving surrounding healthy tissue. Additionally, 3D-printed models allow for the testing of various surgical approaches, reducing the risk of complications during the actual procedure.
Moreover, 3D printing is instrumental in creating personalized treatment options, such as customized radiation therapy. By printing patient-specific molds, radiation doses can be accurately targeted to the tumor, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue and improving the effectiveness of treatment.
3. Orthopedic Applications: Enhancing Bone Surgery and Implants
In the field of orthopedics, 3D printing has demonstrated immense potential in improving the precision of bone surgeries and creating custom implants. In many orthopedic surgeries, such as joint replacements or bone grafts, a mismatch between the prosthetic and the patient’s natural bone structure can lead to complications and prolonged recovery times.
With 3D printing, custom implants and prosthetics can be designed based on the patient’s individual anatomical details. Using 3D scanning techniques, a 3D model of the patient’s bone structure is created, allowing surgeons to design custom-fit implants that match the shape and size of the patient’s bones exactly. This results in more accurate surgeries, faster recovery times, and better long-term outcomes.
In the case of complex fractures, particularly in patients with conditions like osteoporosis, 3D printing can also be used to create patient-specific surgical guides and bone scaffolds. These guides can direct the surgeon in precise positioning during surgery, while the bone scaffolds help promote tissue regeneration and facilitate healing.
4. Dentistry: Customized Solutions for Oral Health
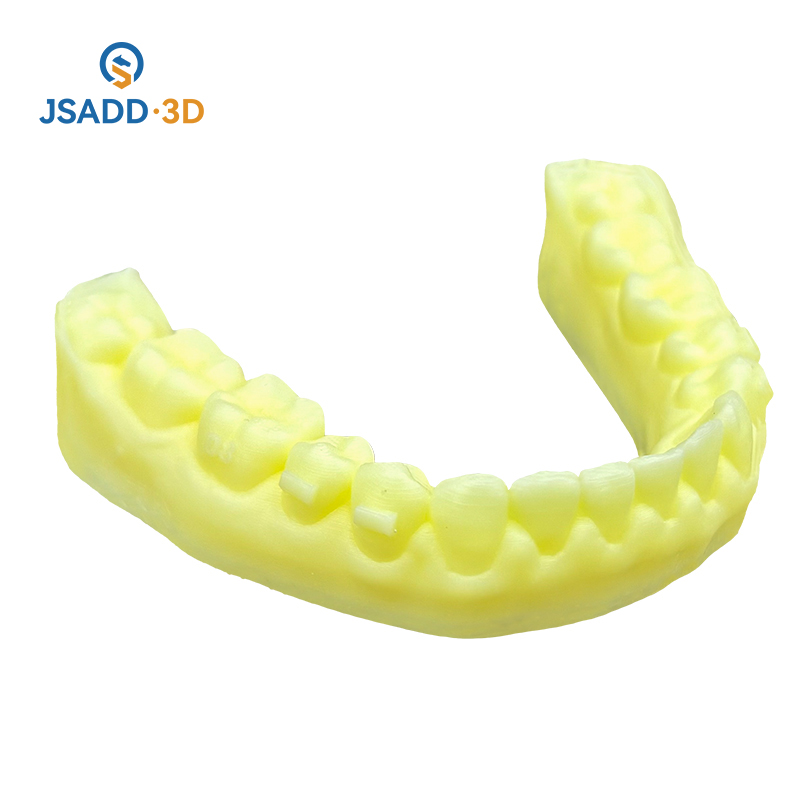
3D printing is also making waves in the field of dentistry, where it is being used to produce custom dental implants, crowns, bridges, and dentures. Traditional methods for creating these dental devices involve the use of molds and manual adjustments, which can be time-consuming and may not always result in a perfect fit. However, with the use of 3D printers, dental professionals can create highly accurate models of a patient’s oral cavity, ensuring a better fit and more natural appearance.
Dental 3D printing services can produce models from digital scans of a patient’s teeth and gums. This allows for the creation of custom dental implants, orthodontic devices, and even full dental arches. These devices are tailored to the unique anatomy of the patient, leading to a more comfortable and effective treatment process. Moreover, 3D printing in dentistry has reduced the time required for producing custom dental devices, which has improved patient satisfaction and reduced the number of follow-up visits.
5. Ophthalmology: Precision in Vision Correction
The application of 3D printing in ophthalmology is another area where precision and customization are essential. For patients with complex eye conditions, such as those requiring corneal implants or prosthetic eyes, 3D printing enables the creation of highly accurate models that match the unique anatomy of the eye.
3D printing allows ophthalmologists to design personalized ocular prosthetics that provide better comfort and functionality compared to traditional methods. For example, the creation of custom prosthetic eyes, based on detailed 3D scans of the patient’s eye socket, ensures that the prosthetic fits seamlessly and moves in alignment with the other eye.
Additionally, 3D printing can assist in creating customized surgical guides for eye surgeries, such as corneal transplants. These guides help surgeons navigate complex procedures with greater precision, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
6. Printing Human Models for Surgical Planning
One of the most groundbreaking uses of 3D printing in healthcare is the ability to print human models for surgical planning. Surgeons can print highly detailed, patient-specific models from MRI, CT scans, or X-ray data. These models provide an incredibly accurate, three-dimensional representation of the patient’s anatomy, enabling the surgeon to plan the surgery in great detail before performing it on the patient.
For example, in cases of complex cardiac surgery or spinal surgery, 3D-printed models allow surgeons to rehearse the procedure, practice navigating the area, and make better-informed decisions about the approach to take. This kind of planning significantly reduces the risk of complications, shortens the time spent in surgery, and enhances overall outcomes.
Moreover, 3D-printed human models are valuable for education and training. Medical students and residents can practice on realistic models before performing surgeries on real patients, helping them build their skills and confidence.
Conclusion
The application of 3D printing in healthcare represents a paradigm shift in how medical professionals approach personalized and precision medicine. From creating customized implants and prosthetics to providing surgeons with detailed models for complex surgeries, 3D printing is transforming the landscape of medical treatment. In oncology, orthopedics, dentistry, and ophthalmology, this technology is helping improve outcomes, reduce risks, and enhance patient satisfaction. As 3D printing services continue to evolve, the future holds even more potential for innovation and breakthroughs in the field of healthcare.