Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)is a powerful 3D printing technology that belongs to the powder bed fusion process family that can produce high-precision and durable parts that can be used directly for end use, small batch production or prototype parts. During the SLS device printing process, small particles of plastic powder are melted into the desired three-dimensional shape using a high-power laser. The laser selectively fuses powder materials by scanning a three-dimensional data section of the surface of the powder bed. After scanning each cross-section, the powder bed is lowered by one layer of thickness, a new layer of material is added to it, and the selective laser sintering process is repeated until the part is complete.
SLS 3D printing can be used both for prototyping functional polymer components and for small production runs because of its high degree of design freedom, high precision, and the production of parts with good and consistent mechanical properties. As following picture shows:
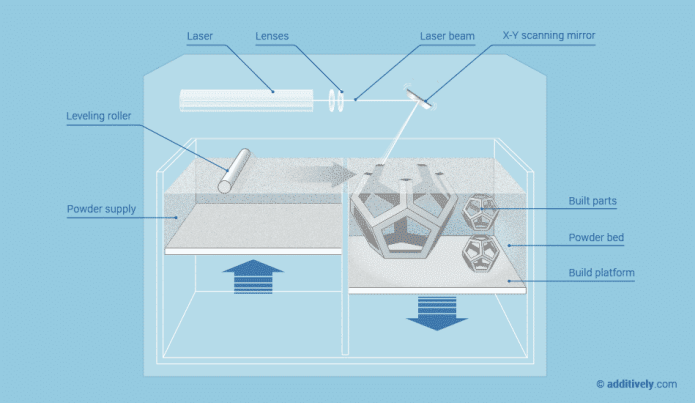 1.Printing Process
1.Printing Process
① First, the silo and the build area are heated to close to the melting temperature of the material, and a layer of powder material is laid.
② A laser is then used to scan the cross-section of this layer, raise the temperature of the powder to the melting point, and selectively sinter the area to be printed to form a bond.
③ After sintering, the build platform moves down, the scraper is coated with another layer of powder material, and the contents of step two are repeated until the entire model is formed.
④ And then after printing, the forming chamber cools down (generally below 40 degrees), and can start to remove the parts for subsequent processing.
2. Features
The main advantage of SLS is that it does not require a support structure. The unsintered powder provides all the necessary support for the part. Therefore, SLS can be used to create free geometric shapes, as long as it is within the parameters of the printing process, designers can use their talents as they wish, without worrying about manufacturing.
When printing with SLS, especially for small batch production, it is important to make the most of the entire build volume and increase the print footprint (the volume ratio of the printed product in the entire print bin). After determining the maximum print height based on the layout needs of the printed products, it will take approximately the same amount of time to print, regardless of the number of printed products in the print control. This is because the spreading speed of each layer determines the total printing time (laser scanning happens very quickly), and the machine will have to cycle through the same number of layers.
Therefore, for a factory that provides SLS process 3D printing services, it can use a large number of orders, and optimize the combination of ordered products as much as possible in the same printing warehouse for production, which will greatly reduce printing costs and increase printing speed. (Reduce the time of waiting for orders and making orders, and quickly start production).
3. Lightweight design considerations
Since SLS does not require support material, parts with hollow sections can be printed easily and accurately.
The hollow part reduces the weight and cost of the part because less material is used, which is especially important in aerospace. Therefore, during the design of the part, or during the processing of data before printing, it is necessary to consider the escape holes of the powder to remove the unsintered powder from the inside of the component (which plays a supporting role in the sintering process). It is recommended to add at least 2 minimum 5 mm diameter escaping holes to your design.
If greater stiffness is required, the part must be printed completely solid. Another option is to make a hollow design, omitting the escape hole. This way, the tightly packed powder will be trapped in the part, increasing its mass and providing some extra support against mechanical loads without affecting build time. An internal honeycomb grid structure can be added to the hollow interior to further increase the stiffness of the component.
4.Advantages and Limitations
a) Key advantages
b) SLS parts have good isotropic mechanical properties, making them ideal for functional parts and prototypes.
c) SLS does not require any support and can easily produce designs with complex geometries.
d) The manufacturing capabilities of SLSare ideal for small and medium-sized batch production.
② Main disadvantages:
a) The surface roughness and internal porosity of SLS parts may require post-processing if a smooth surface or water tightness is desired.
b) The surface roughness and internal porosity of SLS parts may require post-processing if a smooth surface or water tightness is desired.
4.Ending word
JSADD 3D’s SLS/MJF printing technology service is based on nylon HP materials that are commonly used in the market – White/Grey/Black PA12 and MJF PA12 and PA12GB, and is recognized by customers in various overseas countries for high quality.
Contributor: Nina






